While the primary symptoms of gonorrhea typically affect the genital and urinary regions, it is essential to recognize that not all individuals infected with gonorrhea will show visible symptoms.
If symptoms do manifest, they usually arise 2 to 14 days after exposure. Less common or atypical symptoms of gonorrhea could include:
1. Signs of rectal issues include anal itching, discharge from the rectum, and pain or discomfort while having a bowel movement.
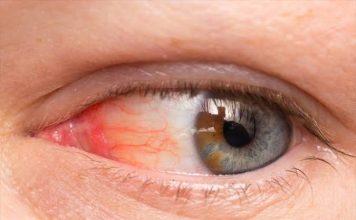
2. Eye symptoms may include conjunctivitis (also known as pink eye), along with redness, itching, or discharge from the eyes.
3. Joint pain or swelling may occur in some cases, known as gonococcal arthritis, although it is not a common complication of gonorrhea.
4. Skin rashes or lesions may develop as well in certain instances.
5. Symptoms related to the throat include a sore throat, inflammation or redness in the throat, and difficulty swallowing.
It is important to note that gonorrhea can be present without any noticeable symptoms. However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and an increased risk of contracting or transmitting HIV.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to gonorrhea or are experiencing any symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Diagnosis typically involves laboratory testing, and treatment usually entails antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
In addition, practicing safe sex, including the use of condoms, is essential to reduce the risk of gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections. Regular STI testing is also recommended, particularly for sexually active individuals or those who engage in high-risk behaviors.